Description
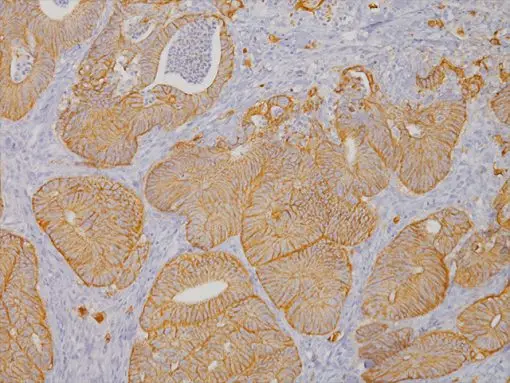
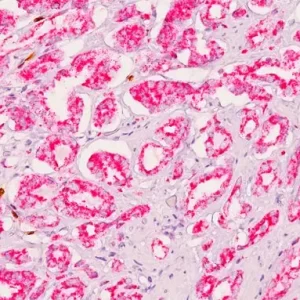
Claudin-4 (Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin receptor) is a tight junction protein encoded by the gene CLDN4. Expression of Claudin-4 has been associated with either poor prognosis or a more favorable diagnosis, depending on the type of cancer. Claudin-4 has been shown to distinguish adenocarcinoma from malignant mesothelioma with 99% specificity in malignant effusions (1). Claudin-4 overexpression was able to independently predict survival in a breast cancer multivariate analysis as it was associated with poor prognosis, high tumor grade and Her2 expression and was inversely correlated with estrogen receptor staining (2). In luminal breast cancer, the increase of Claudin-4 protein was correlated with the increase of tumor grade and with Ki-67, and thus demonstrated an overall shorter life survival (3). Basal-like tumors also demonstrated overexpression of Claudin-4 (4). Counter to the above breast cancer subtypes, the presence of Claudin-4 in triple negative breast cancer was a biomarker that demonstrated a favorable prognosis (3). Loss of Claudin-4 was also seen in 69% of advanced gastric cancers and correlated with poor differentiation (5). Low expression of the Claudin-4 protein correlated with higher T staging, lymphatic metastasis and higher risk of recurrence in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (6). Claudin-4 overexpression in prostate cancer may offer a Claudin-4 targeted therapy as a potential treatment (7).
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| INTENDED USE | IVD |
|---|---|
| FORMAT | Concentrate, Predilute |
| VOLUME | 0.1 ml, 0.5 ml, 6.0 ml |
| SOURCE | Mouse Monoclonal |
| CLONE | 3E2C1 |
| ISOTYPE | IgG1 |
| ANTIGEN | Synthetic peptide corresponding to a 22 amino acid sequence derived from the C-terminal region of human Claudin-4 |
| LOCALIZATION | Cell Membrane |
| POSITIVE CONTROL | Colon carcinoma or breast carcinoma |
DATASHEETS & SDS
REFERENCES
1. Jo VY, Cibas ES, Pinkus GS. Claudin-4 immunohistochemistry is highly effective in distinguishing adenocarcinoma from malignant mesothelioma in effusion cytology. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014 Apr;122(4):299-306.
2. Lanigan F, et al. Increased claudin-4 expression is associated with poor prognosis and high tumour grade in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2009 May 1;124(9):2088-97.
3. Kolokytha P, et al. Claudin-3 and claudin-4: distinct prognostic significance in triple-negative and luminal breast cancer. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2014;22(2):125-31.
4. Lu S, et al. Claudin expression in high-grade invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: correlation with the molecular subtype. Mod Pathol. 2013 Apr;26(4):485-95.
5. Lee SK, et al. Loss of the tight junction protein claudin 4 correlates with histological growth-pattern and differentiation in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2005 Feb;13(2):193-9.
6. Shi M, et al. Low expression of claudin-4: an indicator of recurrence in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after Ivor Lewis esophagectomy? Med Oncol. 2014 May;31 (5):951.
7. Maeda T, et al. Claudin-4-targeted therapy using Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin for prostate cancer. Prostate. 2012 Mar;72(4):351-60.
8. Center for Disease Control Manual. Guide: Safety Management, NO. CDC-22, Atlanta, GA. April 30, 1976 “Decontamination of Laboratory Sink Drains to Remove Azide Salts.”
9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Protection of Laboratory Workers from Occupationally Acquired Infections; Approved Guideline-Fourth Edition CLSI document M29-A4 Wayne, PA 2014.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.