Description
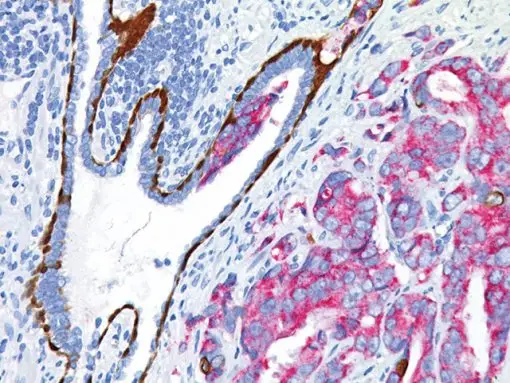
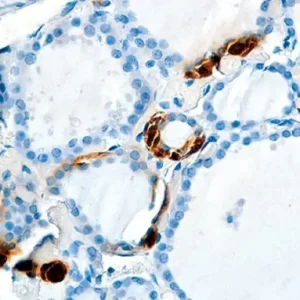
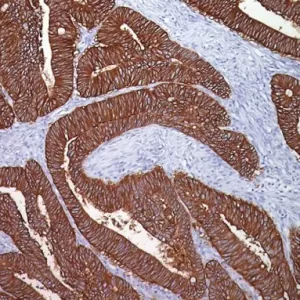
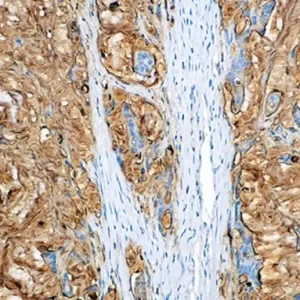
In prostate tissue, mRNA for CK5 and CK14 has been detected in the basal cells of normal glands and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN), a precursor lesion to prostatic adenocarcinoma; however, expression of CK5 or CK14 was not identified in invasive prostatic adenocarcinoma. p63 was detected in nuclei of the basal epithelium in normal prostate glands; however, it was not expressed in malignant tumors of the prostate. In IHC, P504S has been shown to be a specific marker of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Additionally, prostate glands involved in PIN have been found to express P504S, whereas P504S was nearly undetectable in benign glands.
Formerly known as PIN-4®
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| INTENDED USE | RUO |
|---|---|
| SOURCE | Mouse Monoclonal, Mouse Monoclonal, Mouse Monoclonal, Rabbit Polyclonal |
| ISOTYPE | IgG, IgG1/kappa, IgG2a/kappa, IgG3 |
| ANTIGEN | CK14, CK5, P504S, p63 |
| LOCALIZATION | Cytoplasmic, Granular cytoplasm, Nuclear |
| STAINING | Brown (DAB), Brown (DAB), Brown (DAB), Red (Warp Red) |
DATASHEETS & SDS
REFERENCES
1. Tacha DE, Miller RT. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2004 Mar; 12(1):75-8.
2. Tacha DE, et al. Mod Pathol. 2009 Jan; 22(Supplement 1s):388A.
3. Signoretti S, et al. Am J Pathol. 2000 Dec; 157(6):1769-75.
4. Beach R, et al. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002 Dec; 26(12):1588-96.
5. Luo J, et al. Cancer Res. 2002 Apr 15; 62(8):2220-6.
6. Wang Y, et al. Differentiation. 2001 Oct; 68(4-5):270-9.
7. Tokar EJ, et al. Differentiation. 2005 Dec; 73(9-10):463-73.
8. Collins AT, et al. J Cell Sci. 2001 Nov; 114(Pt 21):3865-72.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.