Description
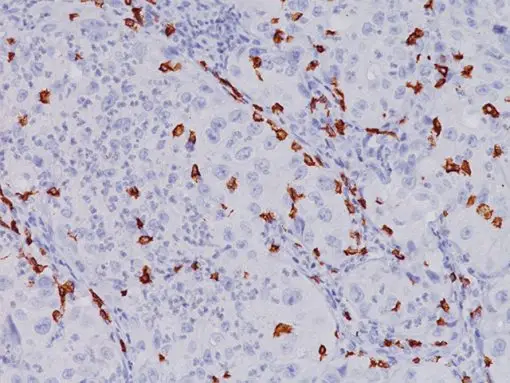
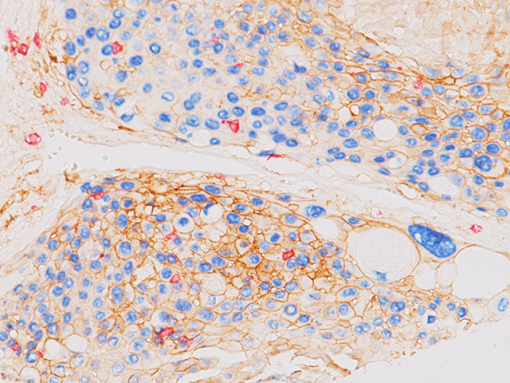
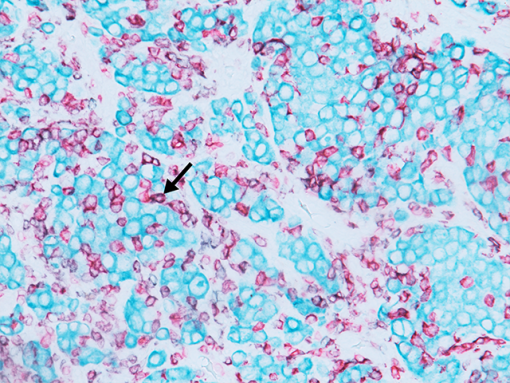
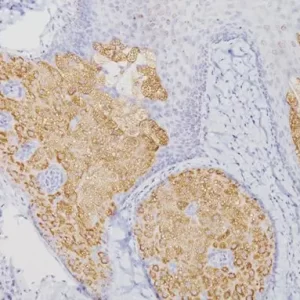
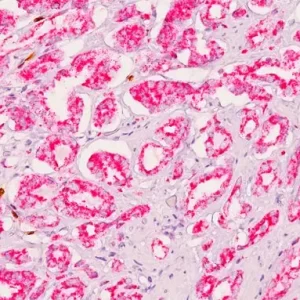
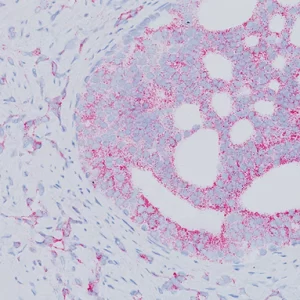
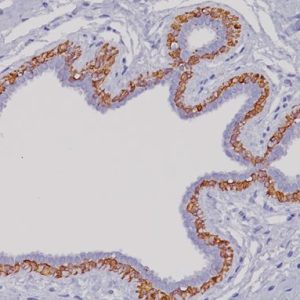
The CD8 antibody reacts with the 32 kDa CD8 protein. CD8 stains cells with cytotoxic activity, including cortical thymocytes, cytotoxic/suppressor T-cells and a subset of natural killer cells. CD4 and CD8 positive and negative staining are indicative of T-cell neoplasms (1-2). CD4 and CD8 may also be used to differentiate between mycosis fungoides and cutaneous inflammatory processes (3-4). CD8 can be used in panels with CD4, CD56, TIA-1 to aid in identifying subsets of inflammatory skin diseases (5). Recently, CD8 has been used in panels with CD103, FOXP3, and PD-l for the identification of CD8+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and their potential value for immune therapy (6-8).
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| INTENDED USE | IVD |
|---|---|
| FORMAT | Concentrate, ONCORE Pro, Predilute, VALENT |
| VOLUME | 0.1 ml, 1.0 ml, 20 ml, 6.0 ml, 60 Tests |
| SOURCE | Mouse Monoclonal |
| CLONE | C8/144B |
| ISOTYPE | IgG1/kappa |
| ANTIGEN | CD8 |
| LOCALIZATION | Cell surface |
| POSITIVE CONTROL | Tonsil and normal Colon |
DATASHEETS & SDS
REFERENCES
1. Barth TF, et al. Primary gastric apoptosis-rich T-cell lymphoma co-expressing CD4, CD8, and cytotoxic molecules. Virchows Arch. 2000 Apr; 436(4):357-64.
2. Williamson SL, et al. New monoclonal antibodies to the T cell antigens CD4 and CD8. Production and characterization in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Am J Pathol. 1998 Jun; 152(6):1421-6.
3. Deguchi M, et al. Proliferative activity of CD8(+) T cells as an important clue to analyze T cell-mediated inflammatory dermatoses. Arch Dermatol Res. 2001 Sep; 293 (9):442-7.
4. Izban KF, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of mycosis fungoides on paraffinembedded tissue sections. Mod Path. 1998 Oct; 11(10):978-82.
5. Harvell JD, Nowfar-Rad M, Sundram U. An immunohistochemical study of CD4, CD8, TIA-1 and CD56 subsets in inflammatory skin disease. J Cutan Pathol. 2003 Feb;30(2):108-13.
6. Webb JR, Milne K, Nelson BH. PD-1 and CD103 are widely coexpressed on prognostically favorable intraepithelial CD8 T cells in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015 Aug;3(8):926-35.
7. Liu S, et al. Prognostic significance of FOXP3+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer depends on estrogen receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 expression status and concurrent cytotoxic T-cell infiltration. Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 6;16(5):432.
8. Tumeh PC, et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature. 2014 Nov 27;515(7528):568-71.
9. Center for Disease Control Manual. Guide: Safety Management, NO. CDC-22, Atlanta, GA. April 30, 1976 “Decontamination of Laboratory Sink Drains to Remove Azide Salts.”
10. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Protection of Laboratory Workers from Occupationally Acquired Infections; Approved Guideline-Fourth Edition CLSI document M29-A4 Wayne, PA 2014.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.